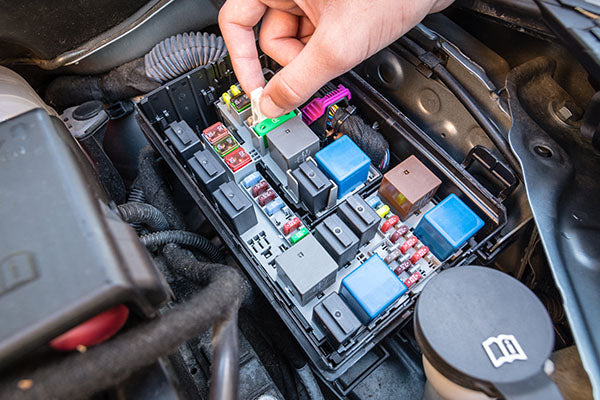
If you've ever experienced an electrical malfunction in your car—whether it’s a radio that won’t turn on, headlights that stay off, or power windows that refuse to budge—there's a good chance you’re dealing with a blown fuse. While this can be a frustrating issue, it’s actually one of the simplest problems to fix. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll show you exactly how to replace a car fuse, and why understanding fuses is essential to maintaining your vehicle’s electrical system.
What is a Fuse and Why is it Important?
Fuses act as protective devices for your car’s electrical circuits. They prevent electrical components from being damaged by an overload or short circuit. A fuse is made of a thin wire or filament that will melt and "blow" when there is too much electrical current passing through it. This opens the circuit and stops the flow of electricity, thereby preventing damage to the electrical components in your car.
Each fuse in your vehicle is designed to handle a specific amount of electrical current (measured in amperes). If a circuit tries to draw more current than the fuse can handle, the fuse will blow, protecting the rest of the car’s wiring and components from potential damage or fire.
What You’ll Need to Replace a Car Fuse:
To successfully replace a blown fuse, gather the following items:
- Replacement fuses: You’ll need the correct type of fuse for your car, with the exact amperage rating as the one you are replacing.
- Fuse puller or needle-nose pliers: A fuse puller is the best tool for removing a fuse safely, but needle-nose pliers can also work if necessary.
- Vehicle owner’s manual: The manual will help you identify the exact location of your fuse box and the correct fuse type for different components in your car.
Step 1: Identify the Problem
Before diving into fuse replacement, ensure that the electrical component in question is truly the source of the issue. Common signs that a fuse has blown include:
- Headlights, tail lights, or brake lights not working
- Power windows, locks, or mirrors malfunctioning
- The radio or infotainment system not turning on
- Interior lights or dashboard lights failing
- The air conditioning or heating system not functioning properly
If any of these components aren’t working, the fuse is the first thing you’ll want to check. Keep in mind that a blown fuse can be caused by something as simple as a loose wire or an overload on the circuit.
Step 2: Locate the Fuse Box
Your car will likely have one or two fuse boxes, one inside the cabin and another under the hood. The location and number of fuse boxes depend on your car’s make and model. To find them:
- Consult the owner’s manual: The manual will tell you exactly where to locate both the cabin and engine compartment fuse boxes.
- Interior fuse box: Typically located under the dashboard near the driver’s side, in the glove compartment, or on the side of the dashboard (where it can be accessed when the door is open).
- Engine compartment fuse box: Often located near the battery or along the side of the engine bay.
In some vehicles, there may be multiple fuse boxes located in different areas, including the trunk or near the wheel well, depending on how the car's electrical system is structured.
Step 3: Identify the Correct Fuse
Now that you've located the fuse box, you’ll need to find the right fuse for the component that isn’t working. Most fuse boxes come with a fuse diagram printed on the inside cover, which will help you quickly locate the correct fuse. The diagram will show you a map of which fuse controls what component, whether it’s the headlights, radio, power windows, or air conditioning.
If the diagram is missing or unclear, your vehicle’s owner’s manual should also contain a list of fuse locations and their corresponding functions. Each fuse has a number indicating its amperage rating, which could range from 5A (amperes) for low-power systems (like the radio) to 30A or more for high-power systems (like headlights or the air conditioning).
Step 4: Inspect the Fuse
Once you've located the correct fuse, inspect it carefully. A blown fuse will typically show one or more of the following signs:
- A broken metal filament: The filament inside the fuse may appear as a thin wire that has been broken or melted.
- Discoloration or blackened areas: Blown fuses often have blackened spots or burn marks indicating that excessive electrical current caused the fuse to blow.
- Cloudy or opaque plastic casing: The fuse's plastic casing may appear cloudy or melted, indicating heat damage.
If you don’t see any visible damage, the fuse may still be functional, and the problem could lie elsewhere.
Step 5: Remove the Blown Fuse
To remove the fuse, use a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed for this purpose) or needle-nose pliers to grip the fuse and pull it out. It’s important to pull the fuse straight out to avoid damaging the fuse box or the surrounding components. Some fuses may be tightly lodged, so apply gentle, even pressure to avoid breaking the fuse.
If you're struggling to remove the fuse, be sure not to force it, as this could cause further damage to the fuse or the fuse box.
Step 6: Install the New Fuse
Before inserting a replacement fuse, double-check the amperage. It’s crucial to use the same amperage rating as the old fuse. Using a fuse with too high of an amperage can cause wiring damage, while one with too low of an amperage could blow again immediately, or worse, lead to electrical failure in your car.
Place the new fuse into the same slot, ensuring that it fits snugly and securely. The fuse should sit flat in the slot with the metal prongs fully inserted into the fuse holder.
Step 7: Test the New Fuse
After replacing the fuse, turn on the car and check to see if the component is working properly. For example:
- If you replaced the fuse for your headlights, test them to ensure they come on.
- If it’s your power windows or radio, try operating those features again.
If the issue persists, the fuse may not have been the cause of the problem. In this case, further troubleshooting or professional assistance may be required.
Step 8: Check for Repeated Blown Fuses
If your new fuse blows shortly after installation, there may be an underlying electrical issue, such as:
- A short circuit: A short circuit occurs when wires become exposed, frayed, or come into contact with metal parts, creating a direct path for electricity to bypass the intended components.
- A faulty electrical component: If the circuit is being overloaded due to a malfunctioning part, the fuse will continue to blow until the faulty component is fixed.
- Overloaded circuit: If you’ve been adding new electrical devices to your car (like aftermarket accessories), the fuse may be insufficient to handle the additional load.
If fuses continue to blow, it's best to take your car to a mechanic who can diagnose and resolve the underlying issue.
Step 9: Keep Spare Fuses on Hand
It’s a good idea to keep a small selection of fuses in your glove compartment or tool kit. This way, if you encounter a blown fuse while driving, you can quickly and easily replace it without the need to visit a repair shop.
Make sure you have a variety of fuses with different amperage ratings, as different circuits in your vehicle require different types of fuses. Your car’s owner’s manual will provide the specifications for all the fuses in your vehicle.
Tips for Maintaining Fuses:
- Regularly inspect fuses: If your car is older or has electrical issues, it's good to check fuses periodically to prevent problems before they arise.
- Use quality fuses: Always replace blown fuses with the correct type and quality of fuse. Inferior fuses can cause electrical problems or even fire hazards.
- Don’t overload your car's electrical system: Avoid adding too many electrical accessories or gadgets to your vehicle without ensuring your electrical system can handle the load.
Replacing a blown fuse is a simple but important task that any car owner can handle. By following this beginner’s guide, you can quickly identify the problem, replace the fuse, and get back on the road. Regularly checking and maintaining your fuses will not only keep your vehicle’s electrical system running smoothly but also save you from expensive repairs. Remember, if a fuse continues to blow, it’s a sign that something more serious is wrong, and you should seek professional help.